DFS and BFS
by mervyn
Graph Traversal
- Process to visit nodes in a graph.
- Traversals of graphs are also called searches.
- How to perform the traversal?
- Breadth-first search (BFS)
- Depth-first search (DFS)
Breadth-First Search (BFS)
Algorithm description
- Choose any vertex, mark it as visited and push it onto queue.
- While the queue is not empty:
- Pop a vertex v from the queue
- For each vertex adjacent to v that has not been visited:
- Mark it visited, and
- Push it onto the queue
- This continues until the queue is empty Note: if there are no unvisited vertices, the graph is connected.
Example
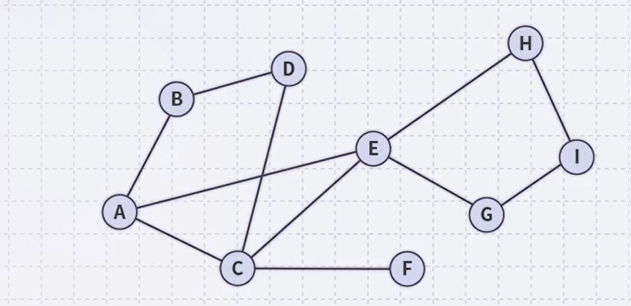
Performing a breadth-first traversal with a queue
- Push the first vertex onto the queue
- Pop A and push B, C and E
- Pop B and push D
- Pop C and push F
- Pop E and push G and H
- Pop D
- Pop F
- Pop G and push I
- Pop H
- Pop I
- The queue is empty: we are done. (A, B, C, E, D, F, G, H, I)
Depth-First Search (DFS)
Algorithm description:
- Choose any vertex, mark it as visited and push it onto stack.
- While the stack is not empty:
- Pop a vertex v from the stack
- For each vertex adjacent to v that has not been visited:
- Mark it visited, and
- Push it onto the stack This continues until the stack is empty
- Note: if there are no unvisited vertices, the graph is connected.
Example
Performing a depth-first search with a stack
- Push A
- Pop A and push B, C, and E
- Pop E and push G and H
- Pop H and push I
- Pop I
- Pop G
- Pop C and push D and F
- Pop F
- Pop D
- Pop B
- The stack is empty: we are done. (A, E, H, I, G, C, F, D, B)
DFS ordering is not necessarily unique.
- e.g.: order to push neighbors to stack could be (A, B, D, C, F, E, G, I, H)
Connected Components
To identify connected components in a graph:
- Perform DFS or BFS.
- Check whether all the vertices are visited or not.
- If not, perform DFS or BFS from one of unvisited vertices until all the vertices are marked as visited.
source “K-MOOC 허재필 교수님의 <인공지능을 위한 알고리즘과 자료구조: 이론, 코딩, 그리고 컴퓨팅 사고> 강좌의 4-1 그래프 탐색: DFS와 BFS 중(http://www.kmooc.kr/courses/course-v1:SKKUk+SKKU_46+2020_T1)”
tags:
Comments
Post comment