Merge Sort
by mervyn
Merge Sort
The merge sort algorithm is defined recursively:
- If the list is of size 1, it is sorted-we are done;
- Otherwise:
- Divide an unsorted list into two sub-lists,
- Sort each sub-list recursively using merge sort, and
- Merge the two sorted sub-lists into a single sorted list This is the first significant divide-and-conquer algorithm we will see.
- Question: How quickly can we recombine the two sub-lists into a single sorted list?
Merging Example
Merge sort contains three things:
- 2 sub-array already sorted,
- 1 combined, merged array that has the output of the 2 sub-array.
- Consider the two sorted arrays and an empty array.
| 3, 5, 18, 21, 24, … |
| 2, 7, 12, 16, 33, … |
- Define three indices at the start of each array.
- Compare 2 and 3: 2 < 3
- Copy 2 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 3 and 7: 3 < 7
- Copy 3 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 5 and 7: 5 < 7
- Copy 5 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 18 and 7: 7 < 18
- Copy 7 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 18 and 12: 12 < 18
- Copy 12 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 18 and 16: 16 < 18
- Copy 16 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 33 and 18: 18 < 33
- Copy 18 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 21 and 33: 21 < 33
- Copy 21 down
- Increment the corresponding indices
Compare 24 and 33: 24 < 33 - Copy 24 down - Increment the corresponding indices
-
Continue until we have passed beyond the limit of one of the two arrays. == One of the sub-arrays gets ended (copied every element from 3 to 31 and there’s no more elements to compare in this sub-array)
-
Copy over all remaining entries in the non-empty array (copy from 33 to 42 sequentially from the second sub-array to the result array)
Merging Two (Sorted) Arrays
Programming a merge is straight-forward:
- the sorted arrays, arrayA and arrayB, are of size nA and nB, respectively, and
- we have an empty array, arrayOut, of size nA+nB
- define three variables, posA = 0, posB = 0, k = 0; which index into these three arrays
Implementation
template <typename Type>
void Merge(Type *_arrayA, Type *_arrayB, int _nA, int _nB, Type *_arrayOut){
int posA = 0, posB = 0, k = 0;
while(posA < _nA && posB < _nB){
if(_arrayA[posA]< _arrayB[posB]){
_arrayOut[k] = _arrayA[posA];
posA++;
}
else{
_arrayOut[k] = _arrayB[posB];
posB++;
}
k++;
}
for(; posA < _nA; posA++){
_arrayOut[k] = _arrayA[posA];
k++;
}
for(; posB< _nB; posB++){
_arrayOut[k] = _arrayB[posB];
k++;
}
}
Problem of Merging
We cannot merge two arrays in-place
- This algorithm always require the allocation of a new array
Algorithm
- Split the list into two approximately equal sub-lists
- Recursively call merge sort on both sub lists
- Merge the resulting sorted lists
Merge-Sort(A, p, r)
if p < r
q = [(p + r)/2]
Merge-Sort(A, p, q)
Merge-Sort(A, q+1, r)
Merge(A, p, q, r)
- Question: We split the list into two sub-lists and sort them. How should we sort these lists?
- Answer(theoretical):
- If the side of these sub-lists is >1, use merge sort again
- If the sub-lists are of length 1, do nothing; a list of length one is sorted
- Answer(practical):
- If the sub-lists are less than some threshold length, use an algorithm like insertion sort to sort the lists
- Otherwise, use merge sort, again
Implementation
Suppose that we already have a function
template <typename Type>
void Merge(Type *array, int first, int midpoint ,int last)
that assumes that the entries
array[first] through array[midpoint - 1], and
array[midpoint] through array[last - 1]
are sorted and merges these two sub-arrays into a single sorted array from index ‘first’ though index ‘last-1’. We will therefore implement a function
template <typename Type>
void Merge_Sort(Type *array, int first, int last)
that will sort the entries in the positions \(first \leq i < last\) If the number of entries is less than \(n_{T}\), call insertion sort Otherwise:
- Find the mid-point
- Call merge sort recursively on each of the halves, and
- Merge the results
template <typename Type>
void Merge_Sort(Type *array, int first, int last){
if(_last - _first <= NUM_THRESHOLD){
Insertion_Sort<Type>(_array, _first, _last);
}// $$T(1)= T(2)= ... = T(N_{T})= \Theta(1)$$
else{
int midpoint=(_first + _last)/2;// $$\Theta(1)$$
Merge_Sort<Type>(_array, _first, midpoint);//$$T\left ( \frac{n-1}{2} \right )$$
Merge_Sort<Type>(_array, midpoint, _last);//$$T\left ( \frac{n-1}{2} \right )$$
Merge(_array, _first, midpoint, _last);// $$\Theta(n)$$ linear time
}
}
Recursive Functions-Merge Sort
Recursion three Given a recurrence: \(T(n)\) = {if \(n = 1\), \(\Theta(1)\) {if \(n > 1\), \(2T(n/2)+\Theta(n)\) We first rewrite the recurrence as follows: \(T(n)\) = {if \(n = 1\), \(c\) {if \(n > 1\), \(2T(n/2) +cn\)
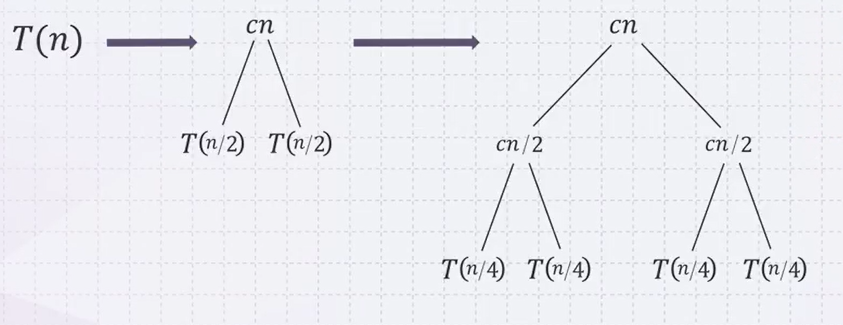

Total Time Complexity: \(\Theta(n lg n)\)
source “K-MOOC 허재필 교수님의 <인공지능을 위한 알고리즘과 자료구조: 이론, 코딩, 그리고 컴퓨팅 사고> 강좌의 7-2 합병 정렬과 재귀적 알고리즘의 복잡도 분석 중(http://www.kmooc.kr/courses/course-v1:SKKUk+SKKU_46+2020_T1)”
tags:
Comments
Post comment