Minimum Spanning Trees: Kruskal's Algorithm
by mervyn
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Sorts the edges by weight and goes through the edges from least weight to greatest weight adding the edges to an empty graph so long as the addition does not create a cycle
- Halting point:
- When \(\lvert V\rvert-1\) edges have been added
- In this case we have a minimum spanning tree
- We have gone through all edges, in which case, we have a forest of minimum spanning trees on all connected sub-graphs
- When \(\lvert V\rvert-1\) edges have been added
Example
- Sort the edges based on weight

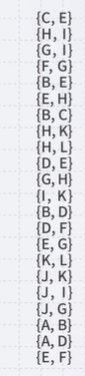
- Starting from the top, check each edge whether it should be included to the minimum spanning tree
- If including an edge does not form a cycle in our minimum spanning tree, we will have the edge added.
- {E,H} coalesces the two spanning sub-trees into one
- {B,C} would create a triangular cycle of B-C-E. Skip {B,C}
- {G,H}, {I,K}, {B,D}, {D,F}, {E,G} creates another cycle. Skip them.
- We can still add edges {J,K} and {A,B}
- Having added {A,B}, we now have 11 edges
- We terminate the loop
- We have our minimum spanning tree
Analysis
The easiest way to check whether there is a cycle or not is to do a graph traversal with DFS or BFS DFS or BFS time complexity is usually proportional to the number of edges: \(O(\lvert E\rvert)\) Amid building trees, the number of edges chosen is less than the number of vertices: \(O(\lvert V\rvert)\)
- Store the edges and their weights in an array
- Sort the edges: \(E\lg E\)
- To determine if a cycle is created, perform a traversal
- A runtime of \(O(\lvert V\rvert)\) Total runtime: \(O(\lvert E\rvert\lg(\lvert E\rvert)+\lvert E\rvert\cdot \lvert V\rvert)\)
- However, \(\lvert E\rvert=O(\lvert V\rvert^{2})\), so \(\lg(\lvert E\rvert)=O(\lg(\lvert V\rvert^{2}))=O(2\lg(\lvert V\rvert))=O(\lg(\lvert V\rvert))\) Final runtime: \(O(\lvert E\rvert\lg(\lvert V\rvert) \lvert E\rvert\lvert V\rvert)=O(\lvert E\rvert\cdot\lvert V\rvert)\) The complexity can be reduced by using “disjoint sets”.
source “K-MOOC 허재필 교수님의 <인공지능을 위한 알고리즘과 자료구조: 이론, 코딩, 그리고 컴퓨팅 사고> 강좌의 11-2 크루스칼 알고리즘 중(http://www.kmooc.kr/courses/course-v1:SKKUk+SKKU_46+2020_T1)”
tags:
Comments
Post comment